Q3 2023 – Australian Economic Overview
November 13th 2023 | , Urban Property Australia
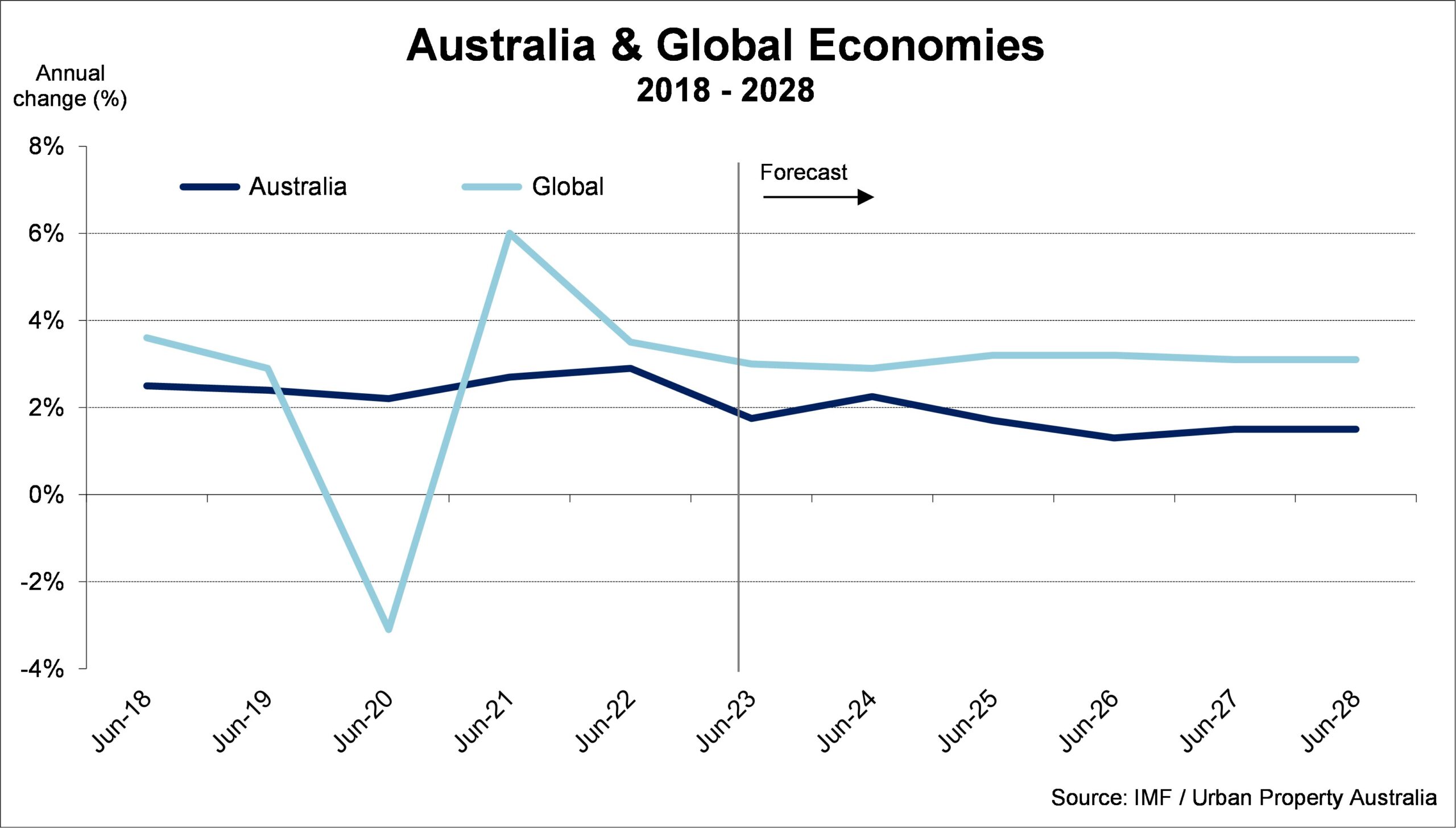
The Australian economy continues to show surprising strength and resilience in a world of growing geopolitical tensions and unrest. While economic activity in Australia continues to weaken as the year progresses, growth has been underpinned by population growth driven by overseas migration which is running at all-time high levels boosting consumption and investment.
Business investment growth has been strong, reflecting a large pipeline of work and an unwinding of supply disruptions. Construction of government infrastructure projects has also contributed to the resilience in overall economic activity. Looking ahead the Australian economy is projected to slow to 1.75% in the 12 months to June 2024 before strengthening to 2.25% 2024/25.
While inflation has been tracking down since its peak in the December quarter 2022, it remains too high and continues to be at the forefront of the Reserve Bank of Australia’s decision making, highlighted by the RBA’s decision to increase official interest rates to 4.35% in November 2023, a 12-year high. Most economists believe that the RBA will rise interest rates further with another rate rise projected for early-2024.
The labour market has eased and is showing more signs of being at a turning point, although the unemployment rate edged downwards to 3.6% in September 2023 from 3.7% in August 2023. The balance between labour demand and supply has continued to improve as more immigrants arrived in Australia, however employment growth appears to be trending down from the average employment growth figures of the past 12 months.
The tight labour market has persisted but is expected to gradually soften in response to slowing demand. Employment growth will be supported by stronger migration which is expected to result in the unemployment rate to increase modestly to 4.25% by mid-2024, and 4.5% by June 2025.
The interest rate hikes are starting to bite with household consumption continued stable through 2023 with household savings continuing to decline, due to higher cost of living eclipsing wage growth. Recent retail sales data suggests discretionary spending has weaken with a rise in non-discretionary expenditure. Consumer sentiment has been at sustained pessimistic levels for more than a year amid high inflation, with consumers remained concerned due to the surprise continued elevated inflation levels.
Looking forward, housing investment is expected to remain subdued in 2023 and potentially 2024 as signalled through the number of dwelling units approvals that has been on a downward trend. In addition, builders continue to experience capacity constraints, high construction and financing costs. Into 2025, strong population growth, anticipated lower interest rates, along with government initiatives to boost supply and the easing in construction input costs, are expected to drive a rebound in dwelling investment.
While business investment has increased through 2023, the majority has been driven by government investment on large-scale transport, health and education projects across several states. Nonetheless, headwinds to business investment continue to gather strength, with weakening consumer demand for goods and services. Costs of non-residential building construction and heavy and civil engineering construction remain high, and elevated interest rates are placing pressures on financing costs.
With Australia recording population growth of 2.4% in the year to June 2023 underpinned with net overseas migration, looking ahead, Australia’s population is forecast to increase by 1.7% next year with net overseas migration remaining above average reflecting the catch up from the pandemic. This strength in migration and population growth is expected to be temporary, with migration forecast to largely return to normal patterns from 2024/25.
Copyright © 2023 by Urban Property Australia All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form, by microfilm, xerography, electronically or otherwise, or incorporated into any information retrieval system, without the written permission of the copyright owner.



